Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a federal program designed to provide financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. The program is administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA) and is funded through payroll taxes. To be eligible for SSDI, an individual must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for a certain number of years, and must have a medical condition that meets the SSA's definition of disability.
Understanding SSDI Eligibility
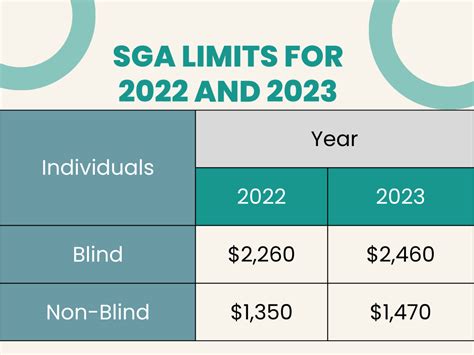
To qualify for SSDI, an individual must meet two main requirements: they must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for a certain number of years, and they must have a medical condition that prevents them from engaging in any “substantial gainful activity” (SGA). The SSA uses a five-step process to determine whether an individual is eligible for SSDI. First, the SSA will determine whether the individual is working and earning above a certain threshold. If they are, they will not be eligible for SSDI. Second, the SSA will determine whether the individual has a severe impairment that significantly limits their ability to perform basic work-related activities. Third, the SSA will determine whether the individual’s impairment is on the SSA’s list of disabling conditions. If it is, the individual will be considered disabled and eligible for SSDI. Fourth, the SSA will determine whether the individual is able to perform any of their past relevant work. If they are, they will not be eligible for SSDI. Finally, the SSA will determine whether the individual is able to perform any other work in the national economy, considering their age, education, and work experience.
SSDI Application Process
The SSDI application process typically begins with an initial application, which can be submitted online, by phone, or in person at a local SSA office. The application will ask for detailed information about the individual’s medical condition, work history, and education. The SSA will then review the application and request additional information, such as medical records and documentation of work history. The SSA may also request that the individual undergo a medical examination by a doctor of their choice. After reviewing all of the evidence, the SSA will make a determination regarding the individual’s eligibility for SSDI. If the individual is found eligible, they will begin receiving benefits after a five-month waiting period.
| SSDI Benefit Amount | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) | The PIA is the base amount of the SSDI benefit, which is calculated based on the individual's earnings record. |
| Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLAs) | COLAs are annual increases to the SSDI benefit amount, which are designed to keep pace with inflation. |
| Dependent Benefits | Dependent benefits are available to the spouses and children of SSDI recipients, and are calculated as a percentage of the recipient's benefit amount. |

Key Points
- SSDI is a federal program that provides financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability.
- To be eligible for SSDI, an individual must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for a certain number of years, and must have a medical condition that meets the SSA's definition of disability.
- The SSA uses a five-step process to determine whether an individual is eligible for SSDI.
- The SSDI application process typically begins with an initial application, which can be submitted online, by phone, or in person at a local SSA office.
- Individuals who are denied SSDI benefits can appeal the decision and may be able to receive benefits after a hearing or further review.
SSDI benefits can be an essential source of financial support for individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. However, the application process can be complex, and it's not uncommon for applications to be denied. By understanding the SSDI eligibility requirements and application process, individuals can better navigate the system and increase their chances of receiving benefits.
SSDI and Work

SSDI is designed to provide financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. However, some individuals may be able to work part-time or in a limited capacity, and may still be eligible for SSDI benefits. The SSA has rules in place to allow individuals to work and still receive SSDI benefits, as long as their earnings do not exceed a certain threshold. For example, in 2022, the SSA considers earnings above $1,350 per month to be “substantial gainful activity” (SGA), and individuals who earn above this amount may not be eligible for SSDI benefits.
SSDI and Other Benefits
SSDI benefits can be coordinated with other benefits, such as Medicare and Medicaid. Individuals who receive SSDI benefits may be eligible for Medicare after a two-year waiting period, and may also be eligible for Medicaid, depending on their income and resources. Additionally, SSDI benefits can be coordinated with other sources of income, such as workers’ compensation and veterans’ benefits.
What is the difference between SSDI and SSI?
+SSDI is a federal program that provides financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability, and is funded through payroll taxes. SSI, on the other hand, is a federal program that provides financial assistance to individuals who are disabled, blind, or elderly, and is funded through general tax revenues.
How long does it take to receive a decision on an SSDI application?
+The length of time it takes to receive a decision on an SSDI application can vary, but it typically takes several months. The SSA will review the application and request additional information, and may also request that the individual undergo a medical examination.
Can I appeal a denial of SSDI benefits?
+Yes, individuals who are denied SSDI benefits can appeal the decision. The appeal process typically involves a hearing with an administrative law judge, and may also involve further review by the SSA's Appeals Council.
In conclusion, SSDI is a vital program that provides financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. While the application process can be complex, understanding the eligibility requirements and application process can help individuals navigate the system and increase their chances of receiving benefits. By coordinating SSDI benefits with other sources of income and benefits, individuals can maximize their financial support and improve their overall well-being.



