The term "circadian" refers to the internal biological processes that occur in living organisms over a roughly 24-hour cycle, influencing various physiological and behavioral aspects. The pronunciation of "circadian" is often a point of interest, as it can vary slightly depending on regional accents and individual speech patterns. The most commonly accepted pronunciation of "circadian" is /sərˈkædiən/ (sər-KAY-dee-ən), with a subtle emphasis on the second syllable.
Understanding Circadian Rhythms

Circadian rhythms are complex processes regulated by an intricate system involving genes, hormones, and environmental cues, particularly light and darkness. These rhythms affect sleep-wake cycles, hormone secretion, eating habits, and body temperature, among other functions. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), a small group of cells in the hypothalamus, acts as the master biological clock, synchronizing the body’s physiological processes with the 24-hour day-night cycle.
Impact of Circadian Rhythms on Health
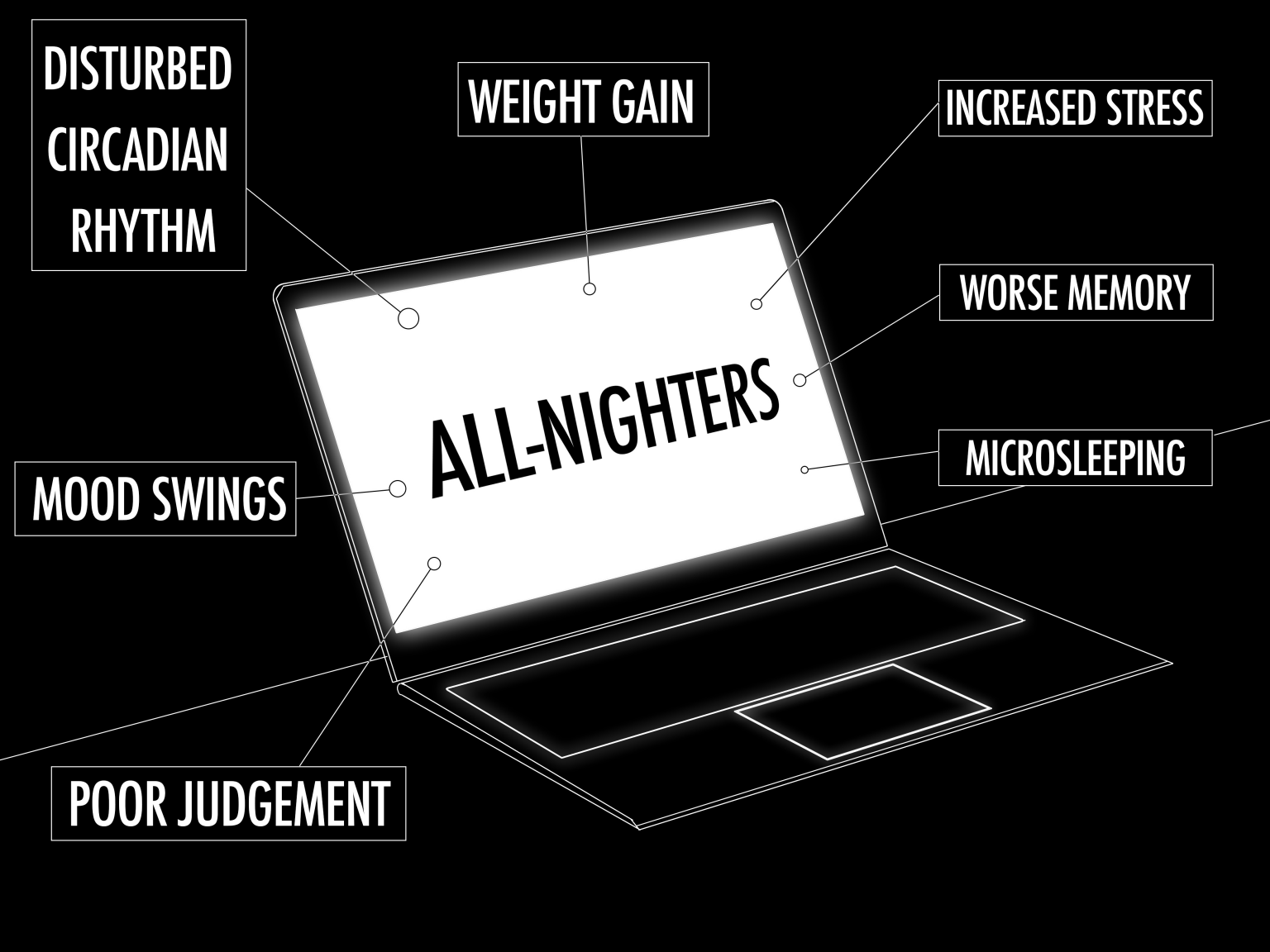
Disruptions to circadian rhythms, such as those caused by shift work, traveling across time zones, or exposure to screens before bedtime, can have significant effects on health. These disruptions can lead to sleep disorders, fatigue, decreased cognitive performance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity. Understanding and respecting the body’s natural circadian rhythms is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
| Aspect of Health | Effect of Disrupted Circadian Rhythms |
|---|---|
| Sleep Quality | Insomnia, daytime fatigue, sleep apnea |
| Metabolic Health | Increased risk of diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome |
| Cognitive Function | Decreased concentration, memory loss, mood disorders |
| Cardiovascular Health | Higher risk of heart disease, stroke, hypertension |
Key Points
- The pronunciation of "circadian" is /sərˈkædiən/ (sər-KAY-dee-ən), with emphasis on the second syllable.
- Circadian rhythms are regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and influenced by light, darkness, and other environmental cues.
- Disruptions to circadian rhythms can lead to sleep disorders, decreased cognitive performance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
- Respecting the body's natural circadian rhythms through consistent sleep schedules, diet, and lifestyle choices is crucial for maintaining health and well-being.
- Understanding the impact of circadian rhythms on health can inform strategies for preventing and managing related disorders.
Further research into the complexities of circadian rhythms and their effects on human health continues to unveil the intricate relationships between our internal biological clocks and the external environment. By acknowledging and adapting to our natural circadian cycles, individuals can take proactive steps towards improving their sleep quality, metabolic health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
What are the primary factors that influence circadian rhythms?
+The primary factors influencing circadian rhythms include light exposure, meal times, sleep schedules, and physical activity. These external cues help synchronize the body's internal clock with the 24-hour day-night cycle.
How do disruptions in circadian rhythms affect mental health?
+Disruptions in circadian rhythms can lead to mood disorders, including depression and anxiety, due to the impact on neurotransmitter regulation and the body's stress response. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and lifestyle can help mitigate these effects.
What strategies can help regulate circadian rhythms?
+Strategies to help regulate circadian rhythms include establishing a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding screens before bedtime, engaging in regular physical activity, and exposing oneself to natural light during the day. A balanced diet and avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime can also support circadian health.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of circadian rhythms and their profound impact on human health is essential for adopting lifestyles that support our natural biological cycles. By recognizing the influence of circadian rhythms on sleep, metabolism, cognitive function, and disease risk, individuals can make informed choices to synchronize their daily habits with their internal clocks, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life.


