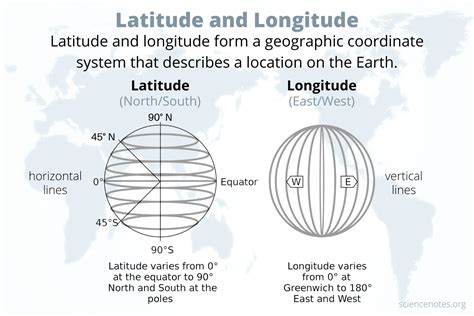
First latitude, a geographical concept that has been a cornerstone of navigation and cartography for centuries, plays a pivotal role in understanding the Earth's layout. The term "latitude" refers to the angular distance of a place north or south of the Earth's equator, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Latitude is a critical component in determining a location's position on the globe, alongside longitude, which measures the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian. The concept of latitude is intricately tied to the Earth's slightly ellipsoidal shape and its rotational axis, which tilts at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees relative to the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
The significance of latitude extends beyond geographical mapping; it influences climate, weather patterns, and even the distribution of flora and fauna across different regions. For instance, areas near the equator, which have a latitude of 0 degrees, tend to have a more consistent and warmer climate throughout the year, while regions at higher latitudes experience more pronounced seasonal changes due to the variation in the amount of sunlight they receive. Understanding latitude is also crucial for navigation, both on land and at sea, as it helps in determining the shortest distance between two points on the surface of the Earth, known as a great circle route.
Key Points
- Latitude is a measure of the angular distance of a place north or south of the Earth's equator.
- It is crucial for navigation and understanding climate and weather patterns.
- Latitude influences the distribution of flora and fauna across different regions.
- Understanding latitude is essential for determining the shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface.
- Latitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, with the equator being 0 degrees latitude.
Geographical and Climatic Implications of Latitude

The geographical implications of latitude are multifaceted. Latitude not only helps in identifying a location’s position but also contributes to the diversity of climates and ecosystems found on Earth. The tropics, which span from 23.5 degrees north to 23.5 degrees south latitude, are characterized by high temperatures and high levels of rainfall, while the polar regions, located at high latitudes, are cold and icy. The variation in latitude is also responsible for the different time zones, with each zone representing a one-hour difference from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) for every 15 degrees of longitude.
Furthermore, the study of latitude has historical significance, dating back to ancient civilizations that recognized the importance of astronomical observations for navigation and agriculture. The ancient Greeks, for example, used the concept of latitude to estimate distances and understand the Earth's shape. Over time, the measurement of latitude has become more precise with the development of advanced astronomical instruments and satellite technology, allowing for accurate cartography and global positioning.
Technological Advancements in Latitude Measurement
The advancement in technology has significantly improved the accuracy and ease of measuring latitude. From traditional methods using celestial navigation, such as observing the position of the Sun, Moon, and stars, to modern GPS (Global Positioning System) technology, the ability to determine one’s latitude has become increasingly accessible. GPS relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, which transmit signals containing their location and the current time. These signals can be received by GPS receivers on the ground, allowing them to calculate their latitude, longitude, and altitude with remarkable precision.
| Method of Latitude Measurement | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Celestial Navigation | Within 1 degree under ideal conditions |
| GPS Technology | Within a few meters |

Latitude in Modern Navigation and Cartography

In modern times, the concept of latitude continues to play a vital role in navigation, both for personal use and in professional fields such as aviation and maritime. The development of digital maps and navigation apps has further simplified the process of determining one’s latitude and navigating between locations. These applications often combine GPS data with detailed maps, providing turn-by-turn directions and real-time traffic updates, making navigation more efficient and user-friendly.
Moreover, the understanding of latitude is essential for climate modeling and meteorological forecasting. By analyzing latitude-specific data on temperature, precipitation, and other climatic factors, scientists can better predict weather patterns and understand the impacts of climate change on different regions. This knowledge is critical for planning and policy-making, especially in areas that are vulnerable to extreme weather conditions or rising sea levels.
Environmental Considerations and Latitude
The relationship between latitude and environmental phenomena is complex and multifaceted. For instance, the latitudinal distribution of solar radiation influences global climate patterns, with areas near the equator receiving more direct sunlight than those at higher latitudes. This variation in solar radiation, in turn, affects the formation of atmospheric circulation patterns, such as trade winds and jet streams, which play a crucial role in shaping regional climates and weather systems.
Additionally, the concept of latitude is intertwined with biodiversity and ecosystem health. Different latitudes support unique ecosystems, ranging from the dense rainforests near the equator to the sparse tundras of the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Understanding these latitudinal variations in biodiversity is essential for conservation efforts and for mitigating the effects of climate change on vulnerable ecosystems.
What is the significance of latitude in navigation?
+Latitude is crucial for navigation as it helps in determining a location's position on the Earth's surface. Along with longitude, it enables the calculation of the shortest distance between two points, facilitating efficient travel and communication.
How does latitude affect climate and weather patterns?
+Latitude significantly influences climate and weather patterns. The amount of solar radiation a region receives, which varies by latitude, affects temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to diverse climates across different latitudes.
What role does latitude play in modern technology and everyday life?
+Latitude plays a pivotal role in modern technology, particularly in GPS systems, which rely on the precise calculation of latitude and longitude to provide location and navigation services. This technology is integrated into various aspects of everyday life, from smartphones and cars to aviation and maritime navigation.
In conclusion, the concept of latitude is fundamental to our understanding of the Earth’s geography, climate, and navigation systems. Its implications are far-reaching, influencing everything from the distribution of flora and fauna to the development of modern navigation technologies. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of latitude in facilitating global communication, travel, and environmental understanding will continue to grow, underscoring the need for a deep and nuanced appreciation of this foundational geographical concept.