Forcing an application to quit is a common troubleshooting step when a program becomes unresponsive or freezes. On Windows, this process is straightforward and can be accomplished through several methods. Understanding how to force quit on Windows is essential for maintaining system stability and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the various techniques for forcing an application to close, including using the Task Manager, the Ctrl+Alt+Del shortcut, and other advanced methods.
Key Points
- Identifying and closing unresponsive applications using Task Manager
- Utilizing the Ctrl+Alt+Del shortcut for quick access to Task Manager
- Alternative methods for force quitting, including command prompt and system configuration
- Preventive measures to avoid application freezes and system crashes
- Troubleshooting techniques for recurring issues with specific applications
Using Task Manager to Force Quit
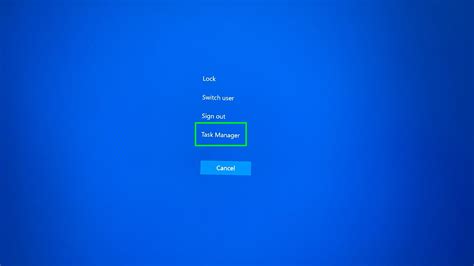
The Task Manager is a powerful tool in Windows that provides a comprehensive overview of running applications, background processes, and system performance. To force quit an application using the Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Press the Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys to open Task Manager directly.
- In the Task Manager window, click on the “Applications” tab.
- Locate the unresponsive application in the list and select it.
- Click on the “End Task” button at the bottom right corner of the window.
This action will force the selected application to close, potentially losing any unsaved data. It’s essential to save your work frequently to avoid data loss in such situations.
Alternative Method: Using Ctrl+Alt+Del
The Ctrl+Alt+Del shortcut offers a quick way to access the Task Manager among other security options. To force quit an application using this method:
- Press the Ctrl+Alt+Del keys simultaneously.
- From the options provided, select “Task Manager” to open it.
- Follow the same steps as before to locate and end the task of the unresponsive application.
This method is particularly useful when you need rapid access to system tools without navigating through the Start menu or searching for Task Manager.
Advanced Methods for Force Quitting

Beyond the graphical interface of Task Manager, Windows provides command-line tools and system configurations that can be used to manage and terminate processes. For advanced users, the command prompt can be a powerful ally in managing system resources.
To force quit an application using the command prompt:
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting “Command Prompt (Admin)”.
- Use the tasklist command to list all running processes.
- Identify the process ID (PID) of the application you wish to terminate.
- Use the taskkill /pid
command, replacing with the actual process ID, to force quit the application.
This method requires familiarity with command-line interfaces and process management, making it more suitable for experienced users.
Preventive Measures and Troubleshooting
While knowing how to force quit applications is useful, preventing them from becoming unresponsive in the first place is even better. Regularly updating your operating system, drivers, and applications can help reduce the occurrence of freezes and crashes. Additionally, ensuring your computer has sufficient resources (RAM, disk space) for the applications you run can prevent overloading and subsequent freezes.
For recurring issues with specific applications, troubleshooting steps such as checking for updates, reinstalling the application, or seeking support from the software developer can be beneficial.
| Application State | Action |
|---|---|
| Unresponsive | Force Quit using Task Manager or Ctrl+Alt+Del |
| Freezing Frequently | Update Application and System, Check for Conflicts |
| Crashing on Startup | Reinstall Application, Check System Logs for Errors |

Conclusion and Future Directions
Force quitting applications on Windows is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through various methods, ranging from the straightforward use of Task Manager to more advanced command-line techniques. By understanding these methods and incorporating preventive measures into your computer maintenance routine, you can enhance your overall computing experience, reduce downtime, and improve system performance. As technology evolves, so too will the methods for managing and troubleshooting applications, making it essential for users to stay informed about the latest tools and best practices.
What happens when I force quit an application?
+When you force quit an application, it immediately closes the program, potentially resulting in the loss of unsaved data. This action is usually taken when an application becomes unresponsive or freezes, preventing normal closure.
How can I prevent applications from becoming unresponsive?
+Regular system and application updates, ensuring sufficient system resources, and avoiding overloading your computer with too many applications can help prevent freezes and crashes. Additionally, maintaining a clean and healthy system through disk cleanups and virus scans is beneficial.
What if force quitting does not work?
+If force quitting an application does not work, you may need to restart your computer. In some cases, underlying system issues may require more advanced troubleshooting or professional assistance to resolve.



